When scientists create vaccines they consider. The vaccine antigen is a hepatitis B virus protein produced by yeast cells into which the genetic code for the viral protein has been inserted.

This graphic made with the Royal Society of Chemistry looks at how they work and highlights other vaccines of this type in use or development for COVID-19.
Viral vector vaccine definition. Viral vector-based vaccines differ from most conventional vaccines in that they dont actually contain antigens but rather use the bodys own cells to produce them. Viral vaccines contain either inactivated viruses or attenuated alive but not capable of causing disease viruses. For COVID-19 viral vector vaccines the vector not the virus that causes COVID-19 but a different harmless virus will enter a cell in our body and then use the cells machinery to produce a harmless piece of the virus that causes COVID-19.
They teach your body how to make a protein that will trigger an immune response. Once inside a cell the viral vector uses this gene and the cells. A broad spectrum of replicating and non-replicating vectors is available.
Much progress has been made towards the development of novel vaccines and vaccination approaches. 1 Like DNA vaccines viral vector vaccines carry DNA into a host cell for production of antigenic proteins that can be tailored to stimulate a range of immune responses including antibody T helper cell CD4 T cell and cytotoxic T lymphocyte CTL CD8 T cell. ChAdOx1 was chosen as the most suitable vaccine technology for a SARS-CoV-2 vaccine as it has been shown to generate a strong immune response from one dose in other vaccines.
It is just the genetic information in it that is different he explains. Delivery of genes or other genetic material by a vector is termed transduction and the. Viral vector-based vaccines constitute a promising part of the biopharmaceutical pipeline addressing many unmet indications.
An appropriate choice for select applications will depend on the biology of the infectious agent targeted as well as fact. Johnson Johnsons vaccine is being studied as a single- and two-dose adenovirus-based vaccine. The Oxford vaccine is a viral vector vaccine which works slightly differently to the RNA vaccines.
They do this by using a modified virus the vector to deliver genetic code for antigen in the case of COVID-19 spike proteins found on the surface of the virus into human cells. In viral vector vaccines a gene unique to the virus being targeted is added to the viral vector. Inactivated or killed viral vaccines contain viruses which have lost their ability to replicate and in order for it to bring about a response it contains more antigen than live vaccines.
Each type is designed to teach your immune system how to fight off certain kinds of germs and the serious diseases they cause. We are writing to express concern about the use of a recombinant adenovirus type-5 Ad5 vector for a COVID-19 phase 1 vaccine study1 and subsequent advanced trials. It is an experimental viral vector vaccine that uses a weakened live pathogen adenovirus as the delivery method vector for transporting a recombinant vaccine for COVID-19.
Viral vector vaccines use a modified version of a different virus the vector to deliver important instructions to our cells. The adenovirus vector for example can be grown up in cells and used for various vaccines. The ChAdOx1 vaccine is a chimpanzee adenovirus vaccine vector.
Vaccines based on viral vectors. Viral vectors are tools commonly used by molecular biologists to deliver genetic material into cellsThis process can be performed inside a living organism or in cell culture Viruses have evolved specialized molecular mechanisms to efficiently transport their genomes inside the cells they infect. Viral vectors have been studied as potential tools to deliver vaccines as they present advantages over traditional vaccines in that they stimulate a broad range of immune responses including cell mediated immunity.
More than 40 vectors are used in the field of viral vectors for gene therapy and vaccines with adenoviruses and modified vaccinia ankara viruses used most frequently for vaccine applications adeno-associated viruses used more commonly for gene therapy and. This is a harmless weakened adenovirus that usually causes the common cold in chimpanzees. Viral vectors provide a convenient means to deliver vaccine antigens to select target cells or tissues.
Over a decade ago we completed the Step and Phambili phase 2b studies that evaluated an Ad5 vectored HIV-1 vaccine administered in three immunisations for efficacy against HIV-1 acquisition23 Both international studies found. Once you make a viral vector it is the same for all vaccines says Florian Krammer a vaccinologist at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. For COVID-19 vaccines this gene codes for the spike protein which is only found on the surface of SARS-CoV-2.
The virus ability to infect cells express large. These vaccines use a virus often weakened and incapable of causing disease itself to deliver a virus antigen into the body. Hundreds of scientific studies of viral vector vaccines have been done and published around the world.
The viral vector is used to shuttle this gene into a human cell. There are several different types of vaccines. Vaccines to prevent human papillomavirus HPV infection also are based on recombinant protein antigens.
Viral vector vaccines combine many of the positive qualities of DNA vaccines with those of live attenuated vaccines. Viral vector vaccines use a harmless virus as a delivery system. The AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine is a viral vector vaccine.
Viral vector vaccines use a harmless virus to deliver genetic code to our cells which make a pathogens protein letting the body develop immunity to new infections. How your immune system responds to the germ Who needs to be vaccinated against the germ The best technology or approach to create the vaccine Based on a number of these.
 Viral Vector Vaccine Design Creative Biolabs
Viral Vector Vaccine Design Creative Biolabs
 What Is A Non Replicating Vaccine
What Is A Non Replicating Vaccine
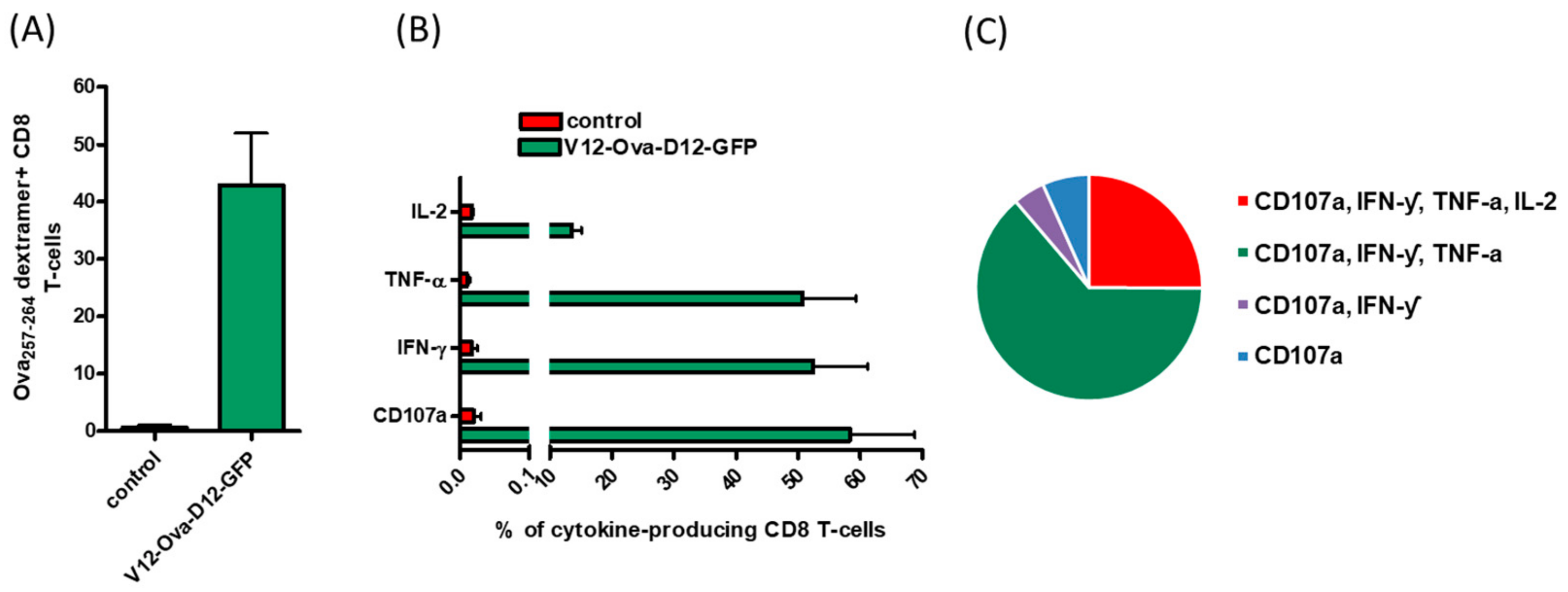 Vaccines Free Full Text Orf Virus Based Vaccine Vector D1701 V Induces Strong Cd8 T Cell Response Against The Transgene But Not Against Orfv Derived Epitopes Html
Vaccines Free Full Text Orf Virus Based Vaccine Vector D1701 V Induces Strong Cd8 T Cell Response Against The Transgene But Not Against Orfv Derived Epitopes Html
 Recombinant Dna Technology An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Recombinant Dna Technology An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Https Repub Eur Nl Pub 112522 Repub 112522 Pdf
Https Www Vdh Virginia Gov Content Uploads Sites 8 2020 12 Vaccination Plan Seminar Slides 20201008 Pdf
 Multivalent And Multipathogen Viral Vector Vaccines Clinical And Vaccine Immunology
Multivalent And Multipathogen Viral Vector Vaccines Clinical And Vaccine Immunology
 Upstream Manufacturing Of Gene Therapy Viral Vectors
Upstream Manufacturing Of Gene Therapy Viral Vectors
 Non Viral Vector An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Non Viral Vector An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Canarypox An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Canarypox An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
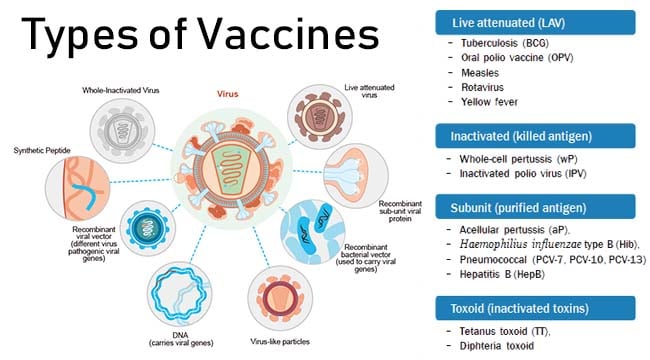 Vaccines Introduction And Types With Examples
Vaccines Introduction And Types With Examples
What Are Viral Vector Based Vaccines And How Could They Be Used Against Covid 19 Gavi The Vaccine Alliance
 What S The Difference Between Active Inactive And Other Types Of Vaccines Meridian Clinical Research
What S The Difference Between Active Inactive And Other Types Of Vaccines Meridian Clinical Research
 Viral And Synthetic Rna Vector Technologies And Applications Molecular Therapy
Viral And Synthetic Rna Vector Technologies And Applications Molecular Therapy
 Sars Cov 2 Vaccine Research And Development Conventional Vaccines And Biomimetic Nanotechnology Strategies Sciencedirect
Sars Cov 2 Vaccine Research And Development Conventional Vaccines And Biomimetic Nanotechnology Strategies Sciencedirect
What Are Protein Subunit Vaccines And How Could They Be Used Against Covid 19 Gavi The Vaccine Alliance
Search This Blog
Blog Archive
- February 2021 (14)
- November 2019 (2)
- October 2019 (5)
- September 2019 (5)
- July 2019 (3)
- June 2019 (7)
- April 2019 (30)
- March 2019 (162)
- February 2019 (2)
- January 2019 (23)
- April 2018 (43)
- February 2018 (46)
- January 2018 (41)
- December 2017 (56)
- November 2017 (249)
- October 2017 (20)
- September 2017 (15)
- July 2017 (3)
- June 2017 (67)
- May 2017 (96)
- April 2017 (65)
- December 2016 (33)
- November 2016 (24)
- September 2016 (78)
- May 2016 (31)
- April 2016 (32)
- December 2015 (64)
- November 2015 (93)
- October 2015 (140)
- September 2015 (963)
- August 2015 (553)
Labels
- 1080p
- 1099
- 1099 Pay Stub Template Free
- 11th
- 12x24
- 1360x768
- 1366x768
- 1767
- 1920s
- 1920x1080
- 1969
- 19th
- 1stockphoto
- 2015
- 2016
- 2018
- 2019
- 2020
- 720x1280
- aarp
- abbey
- abbreviations
- about
- abstract
- academia
- acar
- accord
- account
- accounting
- aceh
- acoustic
- acrylic
- activities
- actress
- adaan
- adalah
- addition
- adhesive
- adidas
- aditya
- adjust
- adjuvanted
- administration
- adonan
- ADP Pay Stub Template Free
- adults
- aerial
- aesthetic
- african
- after
- agency
- ager
- aggarwal
- agreement
- aime
- aircraft
- airplane
- albert
- album
- alcohol
- alexa
- algebra
- alien
- alienware
- allergy
- allianz
- alpha
- alphabet
- alphabetize
- alphabets
- alphonse
- always
- amalfi
- amazing
- amazon
- american
- among
- amount
- anak
- android
- aneka
- angel
- angeles
- animal
- animals
- animated
- anime
- animgif
- anniversary
- another
- answer
- anthropologie
- anti
- antic
- antonio
- apem
- apple
- application
- approval
- apps
- aquatic
- arabic
- architects
- area
- argumentative
- artistic
- asean
- asem
- asian
- asin
- asli
- aspca
- assassins
- assessment
- assets
- attenuated
- auditor
- australia
- authentica
- auto
- availability
- available
- avengers
- awesome
- awug
- ayam
- baba
- babies
- baby
- bacem
- baceman
- back
- backdrops
- background
- backgrounds
- backyard
- baddie
- badminton
- bagel
- bags
- bahan
- bajaj
- bajrang
- bakar
- baking
- bakso
- bakwan
- bali
- ballet
- balloon
- bamboo
- band
- bande
- bands
- bandung
- banjar
- banks
- bape
- barbie
- basah
- based
- basic
- basket
- batao
- bath
- bathroom
- bathtub
- battery
- battle
- bauhaus
- bawang
- beabadoobee
- beach
- bean
- bear
- beautiful
- beauty
- become
- bedding
- bedroom
- beer
- before
- beginners
- beginning
- bekas
- belacan
- belle
- bells
- belong
- beluga
- benefits
- bening
- bentley
- beras
- best
- betawi
- between
- beyond
- bhaiya
- bible
- bieber
- bigger
- bihun
- bike
- bikes
- bikin
- bikinis
- bill
- bingo
- biology
- biome
- birch
- bird
- birds
- birth
- birthday
- black
- blank
- blanket
- blic
- blind
- blog
- blossom
- blossoms
- blue
- bluetooth
- board
- body
- boil
- bold
- bollywood
- bolognese
- bolu
- bong
- book
- boost
- booster
- booty
- bordeaux
- border
- borders
- boston
- boundaries
- bouquet
- bourbon
- boxes
- boys
- bracelets
- bradbury
- branded
- brats
- bread
- breckenridge
- brick
- bridal
- bridge
- bright
- brisbane
- broly
- broncos
- brontak
- brownies
- brushes
- bryant
- buah
- buat
- bubur
- budapest
- buddha
- buffalo
- bugatti
- build
- builder
- buko
- bulan
- bulb
- bulek
- bulk
- bumbu
- buncis
- bunny
- burger
- business
- butler
- butterfly
- butterscotch
- buying
- buzzfeed
- cabinet
- cache
- cactus
- cafe
- cake
- cakes
- cakwe
- calculate
- calculator
- calendar
- california
- calipers
- call
- calm
- calvin
- camaro
- camera
- cameras
- camp
- canada
- canasta
- cancer
- candied
- candle
- candy
- canvas
- capcay
- cara
- card
- cards
- careers
- carpet
- cars
- cart
- cartoon
- case
- casetify
- cashew
- cast
- castle
- catch
- catholic
- cause
- cbr1000rr
- ceiling
- cell
- cellphone
- cellular
- cendol
- cengage
- cenil
- ceramic
- ceremony
- certificate
- chain
- chainsaw
- change
- chapter
- characteristics
- charge
- charging
- charles
- cheap
- cheat
- check
- checkered
- checks
- cheese
- chek
- chelsea
- cherokee
- cherry
- chess
- chevy
- chibi
- chicago
- chicken
- child
- children
- childrens
- chinese
- chip
- choco
- chocolate
- chords
- christmas
- churros
- cigarette
- cimavax
- cincin
- cincinnati
- cinder
- cinema
- circle
- cisalfa
- city
- civic
- class
- classes
- classroom
- classy
- clean
- clear
- climb
- climbing
- clinic
- clipart
- clips
- clouds
- clube
- cneter
- coat
- coats
- coccidiosis
- coco
- coconut
- code
- codes
- coffee
- coffin
- coke
- coklat
- coli
- collage
- color
- colorado
- coloring
- colour
- colouring
- combine
- comforter
- commercial
- common
- companies
- company
- compare
- comparison
- compass
- composite
- comprehension
- compression
- compulsory
- computer
- concrete
- conditioner
- condo
- cone
- connect
- connection
- connects
- conor
- consolidation
- container
- continental
- contract
- Contractor Pay Stub Template Free
- contrast
- controller
- cookies
- cool
- copier
- copyright
- coral
- core
- corndog
- cornell
- corner
- corona
- coronavirus
- corps
- correspondences
- corrosion
- corvette
- cost
- country
- county
- couple
- coupon
- coupons
- cover
- coverings
- covid
- craft
- craigslist
- crashers
- crayon
- cream
- create
- creative
- creed
- creepy
- cricket
- cricut
- crispy
- crossing
- crossword
- crown
- crying
- cubit
- cucut
- cuisinart
- cure
- curriculum
- cursive
- custom
- customer
- cute
- cuties
- cutting
- cycle
- czar
- dadar
- daging
- daily
- dalgona
- damask
- dana
- dancow
- dania
- dari
- dark
- darkrai
- dasar
- database
- date
- dates
- davidson
- dead
- deals
- decal
- decals
- decimal
- deco
- decor
- decorating
- decoration
- deer
- defense
- definition
- degan
- delhi
- dell
- demo
- dental
- denver
- describe
- description
- desert
- design
- designs
- desk
- desktop
- detective
- devi
- device
- devices
- diagram
- dialogue
- diamond
- diamonds
- diana
- died
- different
- digital
- dijual
- dimensions
- dimsum
- directions
- disabled
- disney
- display
- distance
- distribution
- division
- djak
- djum
- dnealian
- docs
- doctors
- dodgers
- does
- dogs
- dokter
- dollar
- donat
- donier
- doodle
- door
- doors
- dorayaki
- down
- download
- dratini
- draw
- drawing
- dreams
- dress
- dresses
- drift
- drive
- drop
- drug
- dulhan
- durga
- duty
- dylan
- ears
- earth
- easter
- eater
- eating
- edge
- edible
- editable
- editor
- eevee
- effect
- effective
- effectiveness
- effects
- eiffel
- einstein
- ekonomis
- elderly
- election
- electivire
- elegant
- elementary
- elephant
- elevated
- elisa
- embossed
- emotional
- empek
- empuk
- enable
- enak
- engagement
- engine
- english
- episodes
- epoxy
- equations
- equine
- escherichia
- español
- espresso
- essay
- etsy
- eureka
- every
- evolution
- evolutions
- evolve
- example
- excel
- exclusive
- exercice
- exercise
- exercises
- exersises
- exotic
- expansion
- experts
- explorer
- explosion
- express
- extinct
- extra
- extraction
- fabric
- face
- facts
- fairy
- fajar
- fake
- fall
- fallout
- Family
- famous
- fantastic
- farm
- farmers
- farmhouse
- fashion
- fashioned
- fast
- fauci
- favor
- fawn
- feature
- fedex
- feet
- felt
- female
- fence
- fern
- fibonacci
- field
- file
- files
- filipino
- fill
- fillet
- film
- filter
- finder
- fire
- fires
- first
- fish
- fishing
- fitness
- flag
- flash
- flatten
- fletcher
- flock
- floor
- floral
- florida
- flour
- flower
- flowers
- flyer
- folder
- following
- fondo
- font
- food
- footage
- football
- force
- ford
- forest
- form
- format
- fortnite
- fourth
- fractions
- fragile
- frame
- framed
- free
- Free Blank Printable Pay Stub Templates
- Free Create Pay Stub Template
- Free Editable Pay Stub Template
- Free Printable Violin Sheet Music Popular Songs
- Free Violin Sheet Music Popular Country Songs
- Free Violin Sheet Music Popular Songs Fiddleman
- freestyle
- french
- friday
- friend
- friends
- friendship
- frock
- from
- frost
- frozen
- fudbal
- fuel
- full
- fundamentals
- funky
- funny
- furniture
- fusion
- gabus
- galaxy
- gallery
- game
- gameinfo
- gameshark
- gaming
- ganesh
- garden
- gardens
- garmin
- gates
- gaun
- gauntlet
- gautam
- general
- generator
- geode
- geometry
- ghost
- giant
- gibson
- giclee
- gift
- gifts
- gilead
- gimbal
- girlfriend
- girls
- girly
- give
- gladiator
- glass
- glencoe
- glitter
- globe
- gloss
- glowforge
- gmail
- godzilla
- gogh
- goku
- gold
- goldblum
- golf
- gomez
- gongso
- gonorrhea
- good
- goodnight
- gooey
- goreng
- gown
- gowns
- grãªmio
- grace
- gracie
- grade
- graders
- graffiti
- grammar
- grand
- grandma
- graphing
- graphs
- grassland
- gray
- grease
- great
- greater
- green
- greige
- grey
- gronkowski
- group
- gudeg
- guide
- guitar
- gula
- gulai
- guna
- gurame
- gutschein
- guys
- gyoza
- hack
- hacked
- haemophilus
- hajatan
- halloween
- hallway
- hamil
- hamilton
- handayani
- hands
- handwriting
- hanging
- hanukkah
- hanuman
- happiness
- happy
- hard
- harga
- harley
- harry
- harvest
- hatchback
- hati
- hatsune
- have
- hawaii
- health
- healthcare
- heat
- heaven
- hedgehog
- heel
- hello
- hepatitis
- herb
- herbivorous
- hero
- heroine
- herpes
- herringbone
- hibernate
- hibernation
- hickies
- hidden
- high
- hijau
- hiragana
- historical
- History
- hitam
- hobbes
- hogwarts
- hokben
- hold
- holiday
- hollywood
- home
- homecoming
- homer
- homeschool
- homeschooling
- homework
- honda
- hong
- horizontal
- Horror
- horse
- horses
- hospitality
- host
- hosta
- hotel
- house
- hulu
- humana
- humans
- hunting
- huracan
- husband
- hutch
- hydrangea
- hypebeast
- iced
- icing
- icon
- ideas
- iggy
- ikan
- illinois
- image
- images
- inconsistent
- increase
- india
- indian
- indiana
- indications
- indonesia
- indoor
- industrial
- industry
- infants
- inference
- infinity
- influenza
- ingredients
- inhale
- injectors
- injured
- inside
- inspirational
- inspired
- instant
- insurance
- interior
- intermediate
- international
- intervention
- intial
- intimate
- inventory
- investigator
- ipad
- iphone
- iphone5
- ipod
- ireland
- iron
- iskcon
- islcollective
- israel
- istanbul
- istep
- istimewa
- istock
- itachi
- items
- jacob
- jadul
- jajanan
- jakarta
- jalar
- jambal
- jamu
- jangan
- japanese
- japonica
- jawa
- jeans
- jeep
- jeff
- jelaskan
- jelly
- jellycat
- jerry
- jesus
- jitsu
- jobs
- joey
- johnson
- johto
- join
- joker
- jolteon
- jordan
- journal
- journey
- jualan
- juegos
- jumbo
- jungle
- justin
- juul
- kacang
- kacangan
- kajal
- kakap
- kakkar
- kampung
- kandungan
- kangkung
- kappa
- kari
- kastengel
- kaur
- kawaii
- kecap
- keep
- keju
- kekinian
- kelapa
- kemangi
- kencur
- kensington
- kentang
- kenyal
- kerang
- kerapu
- kering
- keripik
- kerupuk
- ketan
- ketupat
- keurig
- keyboard
- keypad
- keys
- kids
- kidzone
- kikil
- kill
- kills
- kinder
- kindergarten
- kindle
- king
- kirklands
- kitchen
- kitten
- knot
- know
- kobe
- kohls
- kong
- korea
- kornet
- korra
- krim
- krishna
- kuah
- kukus
- kulit
- kumon
- kuning
- kurma
- kuwe
- laba
- labu
- ladies
- lake
- lakh
- lakshmi
- lambangnya
- lamborghini
- lamongan
- lamp
- lampu
- land
- landscape
- landscaping
- lapis
- laptop
- laptops
- large
- last
- latest
- lava
- lavender
- lavora
- lawn
- lawsuit
- laxmi
- layout
- leaf
- learning
- lease
- leather
- lebaran
- ledis
- left
- legend
- legendary
- legends
- legs
- lehenga
- lembut
- lengko
- letter
- lettering
- letters
- level
- lexus
- liability
- library
- liem
- life
- light
- lights
- lilac
- line
- linen
- lines
- lining
- lion
- liquidators
- list
- lists
- litter
- little
- live
- living
- liwet
- lizards
- llama
- location
- locations
- login
- logo
- logos
- logotipo
- london
- long
- lontong
- look
- looking
- lord
- louisiana
- lounge
- love
- luciferase
- luckin
- lucu
- luxury
- lyme
- lyrics
- maca
- macam
- macaroon
- macbook
- machine
- macrame
- made
- madison
- magelang
- magic
- maine
- maison
- make
- makelike
- maker
- making
- male
- mammals
- manado
- mandala
- mandarinia
- mandatory
- manger
- mangga
- mangkok
- manis
- manisan
- manual
- many
- maps
- marble
- marilyn
- marine
- mario
- marmer
- maroon
- marry
- martabak
- masak
- masakan
- masculine
- mason
- master
- mata
- matahari
- mataji
- math
- matrix
- mattress
- maxi
- mbok
- mcgregor
- mcqueen
- meaning
- meanings
- means
- measles
- measure
- measurement
- mechanical
- medan
- medical
- meets
- mehandi
- melanoma
- membuat
- meme
- memes
- mendoan
- meningitis
- menjeng
- mens
- mentega
- menu
- merah
- merge
- mermaid
- metal
- mete
- michaels
- michigan
- microsoft
- microwave
- midnight
- mijello
- miku
- mild
- mileage
- milk
- milo
- minecraft
- mini
- minuman
- minute
- mirzapur
- mission
- mixer
- mnemonic
- mobile
- model
- modeling
- modern
- moderna
- moles
- molly
- monday
- money
- monitor
- monroe
- moon
- moose
- most
- motivation
- motorcycle
- mountain
- mountains
- mouse
- movie
- moving
- mpasi
- mrna
- much
- mucha
- mudah
- mudge
- mugs
- multiplication
- murah
- mural
- murals
- muscle
- musharna
- Music
- mutant
- mute
- myford
- myth
- naga
- nama
- name
- nanoparticle
- narayan
- narrow
- naruto
- nasi
- nastar
- nationalism
- native
- nativity
- nature
- nautical
- navajo
- navdurga
- navy
- near
- necktie
- need
- needle
- neha
- neon
- nescafe
- nespresso
- netflix
- neutral
- News
- nice
- nick
- night
- nike
- nila
- ninja
- nissan
- noah
- nonprofit
- norman
- norte
- north
- notary
- note
- notebook
- notification
- nouns
- novembre
- number
- numbers
- nurse
- nursery
- nutrition
- nutritional
- oasis
- obat
- ocean
- office
- official
- often
- ohio
- olahan
- olympics
- ombre
- onde
- online
- open
- orange
- order
- oreo
- organizer
- oriental
- origin
- originals
- orlando
- oseng
- outdoor
- outlet
- outlook
- outside
- oven
- over
- oversized
- oxygen
- pack
- pages
- pain
- paint
- painting
- paintings
- paints
- pakai
- palsy
- pancake
- pancong
- pandan
- panel
- panoramic
- panther
- pantone
- paper
- paperwhite
- para
- paragraph
- paria
- parions
- paris
- parivar
- park
- parker
- parts
- pass
- password
- past
- pasta
- pastel
- patch
- patike
- patio
- patricia
- pattern
- patterns
- payouts
- peacock
- peda
- peel
- peeling
- pelangi
- pemdas
- pempek
- pencil
- pencils
- pengertian
- pentol
- peonies
- peony
- pepes
- perennial
- period
- personalized
- perth
- petis
- pets
- pfizer
- phoenix
- phone
- phones
- phonics
- photo
- photography
- photos
- photoshop
- pics
- picture
- pictures
- piece
- pier
- pillowfort
- pillows
- pindang
- pine
- pineapple
- pink
- pirate
- pirex
- pisang
- pixel
- pixelmon
- place
- plain
- planet
- planner
- plans
- plant
- plants
- plaques
- plated
- plates
- play
- playlist
- playstation
- plein
- plug
- plus
- pneumonia
- pocoyo
- poem
- pokemon
- policy
- polio
- polynesian
- pool
- pornhub
- porsi
- portfolio
- portrait
- positive
- posters
- potatoes
- potter
- powder
- ppsv23
- practice
- practitioner
- praktis
- pray
- prefixes
- pregnant
- prek
- premium
- preparez
- preschool
- preschoolers
- prestige
- pretty
- price
- pricelist
- pride
- princess
- printable
- printables
- printer
- prints
- prism
- privacy
- produce
- production
- program
- promo
- promoters
- prompts
- propose
- protect
- publish
- puding
- pukis
- pulsar
- pumpkin
- pumpkins
- pumps
- puppy
- pura
- purchase
- purple
- purwokerto
- putih
- puzzles
- pyramid
- quadratic
- quadrilaterals
- quaker
- quality
- quantum
- queen
- quest
- quickly
- quilted
- quinn
- quinoa
- quote
- quotes
- quotient
- rabbit
- rabies
- race
- radha
- radhe
- raid
- railroad
- rain
- rainbow
- rainforest
- raised
- raleigh
- rapuh
- rare
- rayner
- rays
- reaction
- read
- readiness
- reading
- real
- reasons
- reboot
- reception
- recipe
- reconstruction
- record
- recycled
- redwood
- refinish
- refresh
- regal
- region
- register
- registry
- release
- remodeling
- remote
- removable
- removal
- remove
- remover
- rendang
- rental
- rentals
- renyah
- replace
- reprezentacija
- repsol
- rescue
- research
- resep
- resin
- resolution
- respiration
- restart
- retaining
- retro
- reusable
- reveal
- rfid
- rica
- riddle
- rifle
- ring
- rings
- risoles
- rock
- rockwell
- rogue
- roku
- rolade
- roles
- roll
- romantic
- roof
- room
- rose
- roses
- ross
- roti
- rover
- royalty
- royco
- rubicon
- rufflet
- rujak
- ruler
- rules
- rumahan
- running
- russia
- rustic
- sable
- safari
- safe
- safety
- sagu
- sala
- salad
- sale
- sales
- salle
- salute
- samarinda
- sambal
- same
- sample
- samples
- sams
- samsung
- sans
- santan
- santos
- sapi
- sapphire
- sarang
- sarnia
- sate
- saus
- save
- sawi
- saxon
- sayur
- scandal
- scene
- scenes
- scenic
- schedule
- science
- sconces
- scottish
- screen
- screensaver
- screensavers
- script
- sculpture
- seafoam
- search
- seashell
- season
- seasons
- seblak
- second
- secret
- secure
- security
- sederhana
- seel
- segar
- selatan
- selena
- self
- semarang
- semi
- semut
- send
- seniors
- sensual
- sentence
- sentences
- sequence
- serangan
- serealia
- serenity
- series
- service
- services
- setengah
- sets
- seven
- shade
- shakespeare
- shape
- share
- sheet
- sheets
- sherawali
- shield
- shift
- shingles
- shipping
- shirt
- shiv
- shiva
- shoes
- shop
- shops
- Short
- shot
- should
- shoulder
- show
- shower
- shree
- shri
- sick
- side
- siemens
- sight
- sign
- signature
- signs
- silk
- silver
- silvia
- simping
- simple
- singapore
- singer
- singkong
- siobak
- siomay
- sirup
- sirva
- sites
- sitting
- size
- sizer
- skateboard
- skin
- skinny
- skyline
- skype
- sleeping
- sleeves
- slideshow
- slime
- slippers
- small
- smart
- smartphone
- smoke
- snapchat
- sneakers
- snorlax
- snowfall
- sofa
- software
- solo
- solon
- song
- songs
- sonntag
- sony
- soothing
- sophisticated
- sorority
- soto
- sotong
- soul
- sound
- soundbar
- sounds
- soundtrack
- source
- south
- space
- spark
- speaker
- speakers
- special
- spelling
- spesial
- splash
- split
- spoof
- Sport
- sportrs
- sports
- square
- star
- starburst
- stars
- start
- starter
- state
- status
- stay
- steak
- steam
- steamer
- steel
- steelers
- steep
- step
- stick
- sticker
- stickers
- stik
- stiletto
- stilettos
- stock
- stockholm
- stone
- store
- stores
- story
- strangles
- strawberry
- stream
- strip
- stripe
- strongest
- structure
- student
- study
- stuff
- stuffed
- stump
- stup
- style
- stylish
- subjective
- succulent
- suffixes
- summarizing
- sunda
- sunday
- sunflower
- sunset
- super
- superhero
- supply
- surabaya
- susu
- suwir
- swami
- swamy
- sweet
- swim
- swimwear
- switch
- sword
- syllable
- symptoms
- sync
- system
- table
- tablet
- tacoma
- tahu
- tahun
- take
- tamil
- tampa
- tangled
- tank
- tanpa
- tape
- tapestry
- tattoo
- tawar
- taxes
- teacher
- teachers
- teal
- team
- teams
- technology
- teddy
- teen
- teeth
- teflon
- television
- tell
- telur
- tempe
- templ
- template
- templates
- tenggorokan
- terang
- teri
- terigu
- teriyaki
- tesla
- test
- tetanus
- texas
- text
- texture
- thailand
- thanksgiving
- theater
- their
- theme
- themed
- then
- therapeutic
- there
- thin
- things
- third
- this
- throw
- thursday
- tickets
- ticking
- tighten
- tiktok
- tile
- tiles
- time
- timed
- timeline
- times
- timun
- tint
- tintin
- tips
- tiram
- tires
- toddler
- toddlers
- tomat
- tongkol
- tool
- tooth
- tote
- touch
- towel
- towels
- tower
- toyota
- toys
- tracing
- tracker
- tracking
- train
- transfer
- transparan
- transparent
- travel
- treated
- tree
- trees
- trek
- trending
- trial
- triangular
- tribal
- tropical
- trusses
- tsheets
- tumblr
- tumis
- tundra
- tune
- turbo
- turkey
- turn
- turtle
- turtles
- tuscan
- tutorial
- twinrix
- twitch
- type
- types
- udaipur
- udang
- uefa
- ukulele
- ukuran
- ulat
- ultra
- under
- understanding
- underwater
- unearned
- unemployment
- uneven
- ungkep
- unicorn
- unique
- unit
- university
- unlimited
- unlocked
- unsplash
- untuk
- update
- used
- user
- using
- uživo
- vaccinate
- vaccinated
- vaccination
- vaccinations
- vaccine
- vaccines
- valentine
- valentines
- valhalla
- valuable
- value
- vans
- varicella
- vasco
- vector
- vegan
- vegetable
- veggie
- venkateswara
- venue
- verbs
- verse
- vertical
- vespa
- vetera
- vibes
- victoria
- video
- videos
- vinci
- vintage
- vinyl
- Violin Music Sheets Free Popular Songs Easy
- viral
- virginia
- vocabulary
- volcanoes
- voltage
- volvulus
- voting
- vrbo
- waiting
- walking
- walkway
- wall
- wallet
- wallpaper
- wallpapering
- wallpapers
- walls
- walmart
- walnut
- walt
- wanderlust
- warren
- wars
- wash
- washington
- wasp
- watch
- watches
- water
- watercolor
- watercolors
- waterfall
- watermark
- waves
- wayfair
- wear
- website
- websites
- wedding
- wednesday
- welcome
- went
- west
- what
- wheelbarrow
- when
- where
- whipped
- white
- whiten
- wide
- wifi
- wild
- wildfires
- wildflowers
- wildlife
- will
- williams
- windmill
- window
- windows
- winslow
- wireless
- wisdom
- wishes
- with
- woku
- wolf
- wolverine
- woman
- women
- wontumi
- wood
- wooden
- word
- words
- work
- workers
- worksheet
- worksheets
- world
- worried
- wortel
- worth
- wound
- wrangler
- write
- writing
- wrought
- wuri
- ximilu
- xmas
- yang
- yantra
- yard
- yards
- year
- years
- yeezy
- yeezys
- yellow
- york
- young
- your
- yourself
- youtube
- zaner
- zebra
- zenske
- zombies
- zoom
-
Black woman in bikini stock pictures royalty-free photos. As always send in all your best photos via iChive OR you can ALSO send pics in thr...
-
Unless you have severe symptoms you can most likely treat them at home the. The aim of treatment is to manage and reduce symptoms until you ...
-
Reusable Removable Wallpaper 25 Off For A Limited Time The Chronicles Of Home Removable Wallpaper Bedroom Temporary Wallpaper Rental Decor...


